围绕沃尔夫-拉叶星18的不对称星云
(原标题: The Asymmetric Nebula Surrounding Wolf-Rayet Star 18)
2022-11-09
浏览次数: 17
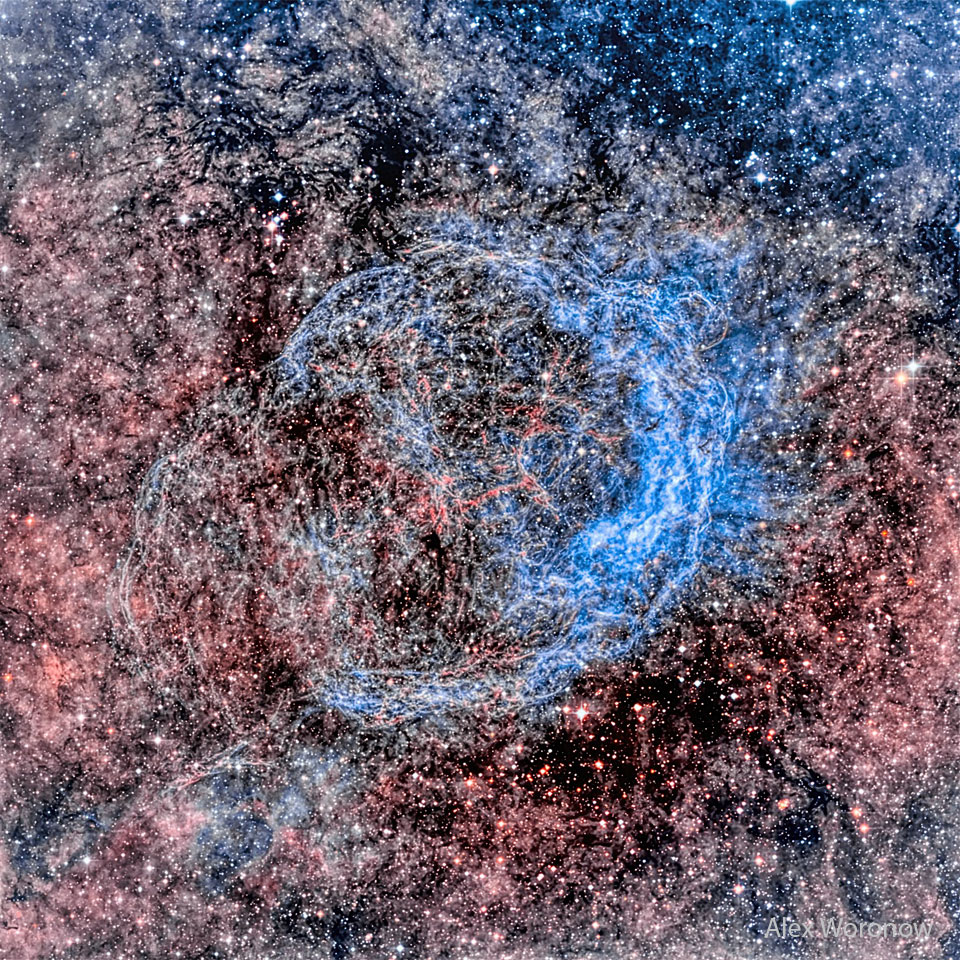
为什么围绕恒星WR-18的星云有一面更亮?这颗活跃的恒星也被称为NGC 3199,它和周围的星云位于12000光年外的船底座。这张特色的深度图像经过了高度处理,以显示出气泡状星云中发光气体的细丝细节。该星云直径约75光年。星云中心附近有一颗沃尔夫-拉叶星WR-18,这是一颗巨大、炽热、寿命短的恒星,它会产生强烈而复杂的恒星风。事实上,众所周知,沃尔夫-拉叶星在强大的风扫过周围的星际物质时,会产生形状有趣的星云。在这种情况下,明亮的右侧边缘最初被认为是恒星在穿过均匀介质时产生的弓形激波,就像船在水中一样。然而,最近的测量和分析表明,这颗恒星并没有迅速向明亮的边缘移动。一种更可能的解释是,恒星周围的物质不是均匀的,而是聚集在明亮边缘附近,密度更大。
查看原文解释
Why does the nebula around the star WR-18 shine brighter on one side? Also known as NGC 3199, this active star and its surrounding nebula lie about 12,000 light-years away toward the nautical southern constellation of Carina. The featured deep image has been highly processed to bring out filamentary details of the glowing gas in the bubble-shaped nebula. The nebula is about 75 light-years across. Near the nebula's center is a Wolf-Rayet star, WR-18, which is a massive, hot, short-lived star that generates an intense and complex stellar wind. In fact, Wolf-Rayet stars are known to create nebulas with interesting shapes as their powerful winds sweep up surrounding interstellar material. In this case, the bright right edge was initially thought to indicate that a bow shock was being produced as the star plowed through a uniform medium, like a boat through water. Recent measurements and analyses, however, have shown the star is not moving quickly toward the bright edge. A more likely explanation has emerged that the material surrounding the star is not uniform, but clumped and denser near the bright edge.
© Alex Woronow