哈勃的木星和正在缩小的大红斑
(原标题: Hubble's Jupiter and the Shrinking Great Red Spot)
2022-01-09
浏览次数: 14
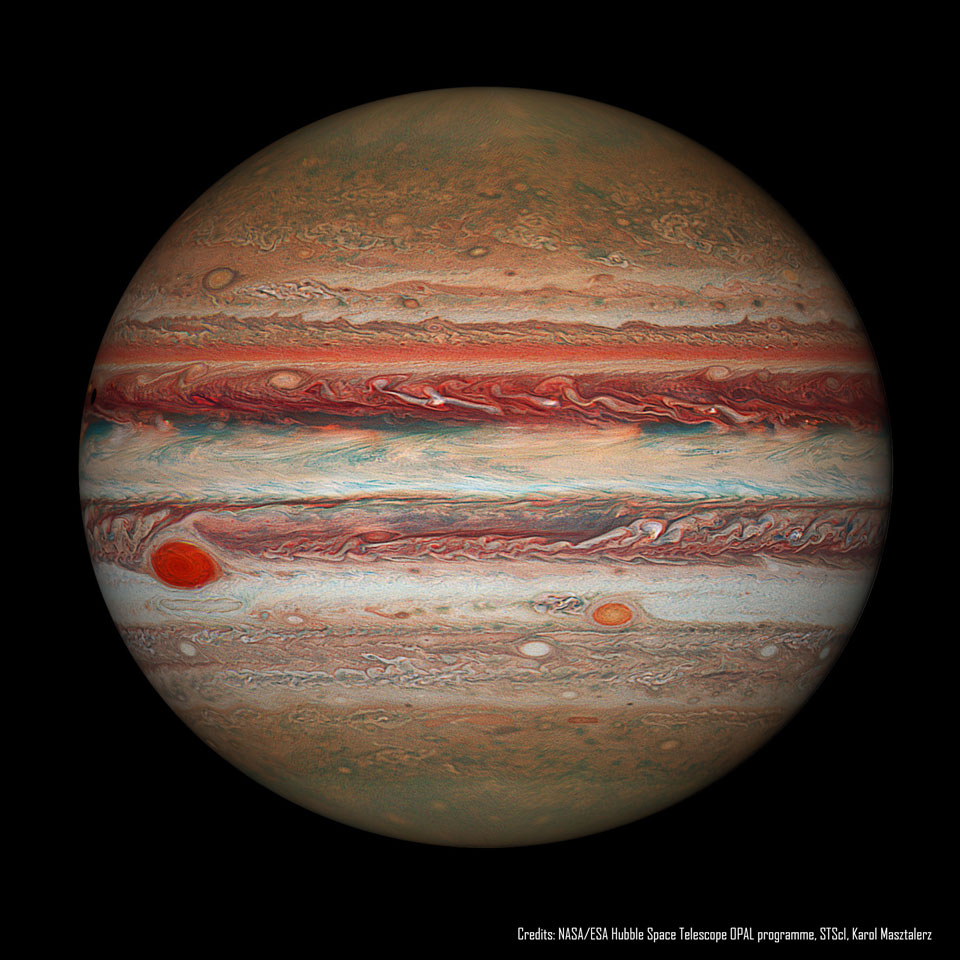
木星的大红斑会变成什么样子?气态巨行星木星是太阳系中最大的行星,质量大约是地球的320倍。木星是已知的最大和持续时间最长的风暴系统之一的家园,大红斑(GRS),在左边可见。GRS是如此之大,以至于它可以吞没地球,尽管它一直在缩小。与历史记录相比,这次风暴的覆盖面积只有150年前的三分之一。美国宇航局的外行星大气遗产(OPAL)项目最近一直在使用哈勃太空望远镜监测这场风暴。哈勃OPAL望远镜拍摄的这张特色图片显示了木星在2016年的样子,处理后的红色色调显得非常鲜艳。现代GRS数据表明,风暴继续缩小其表面面积,但垂直方向也略有升高。没有人知道GRS的未来,包括如果萎缩趋势继续下去的可能性,GRS可能有一天甚至会像木星上较小的斑点那样完全消失。周二在Zoom上:APOD编辑将呈现2021年最佳APOD空间图像
查看原文解释
What will become of Jupiter's Great Red Spot? Gas giant Jupiter is the solar system's largest world with about 320 times the mass of planet Earth. Jupiter is home to one of the largest and longest lasting storm systems known, the Great Red Spot (GRS), visible to the left. The GRS is so large it could swallow Earth, although it has been shrinking. Comparison with historical notes indicate that the storm spans only about one third of the exposed surface area it had 150 years ago. NASA's Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program has been monitoring the storm more recently using the Hubble Space Telescope. The featured Hubble OPAL image shows Jupiter as it appeared in 2016, processed in a way that makes red hues appear quite vibrant. Modern GRS data indicate that the storm continues to constrict its surface area, but is also becoming slightly taller, vertically. No one knows the future of the GRS, including the possibility that if the shrinking trend continues, the GRS might one day even do what smaller spots on Jupiter have done -- disappear completely. Tuesday over Zoom: APOD editor to present the Best APOD Space Images of 2021